Apex
Apex is a strongly typed, object-oriented programming language that allows developers to execute flow and transaction control statements on Salesforce servers in conjunction with calls to the API. Using syntax that looks like Java and acts like database stored procedures, Apex enables developers to add business logic to most system events, including button clicks, related record updates, and Visualforce pages. Apex code can be initiated by Web service requests and from triggers on objects.
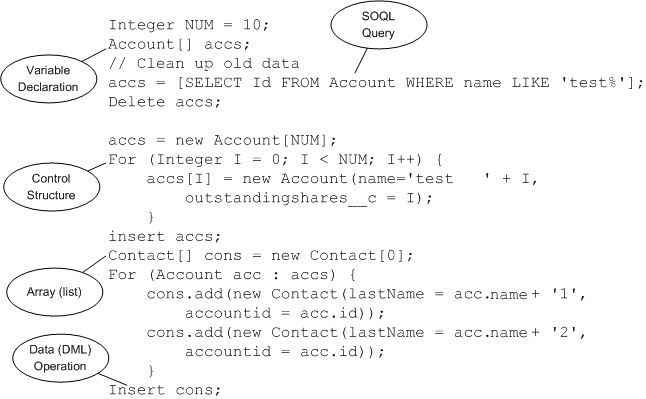

When a developer writes and saves Apex code to the platform, the platform application server first compiles the code into an abstract set of instructions that can be understood by the Apex runtime interpreter, and then saves those instructions as metadata.
When an end user triggers the execution of Apex, the platform application server retrieves the compiled instructions from the metadata and sends them through the runtime interpreter before returning the result. The end user observes no differences in execution time from standard platform requests.
Apex can be used to:
- Create Web services.
- Create email services.
- Perform complex validation over multiple objects.
- Create complex business processes that are not supported by workflow.
- Create custom transactional logic (logic that occurs over the entire transaction, not just with a single record or object).
- Attach custom logic to another operation, such as saving a record, so that it occurs whenever the operation is executed, regardless of whether it originates in the user interface, a Visualforce page, or from SOAP API.
Apex cannot be used to:
- Render elements in the user interface other than error messages
- Change standard functionality
- Apex will prevent this functionality from happening, or add additional functionality
- Create temporary files
- Spawn threads
Writing tests
Testing is the key to successful long-term development and is a critical component of the development process. We strongly recommend that you use a test-driven development process, that is, test development that occurs at the same time as code development.
Apex supports the creation and execution of unit tests.
- Unit tests are class methods that verify whether a particular piece of code is working properly.
- Unit test methods take no arguments, commit no data to the database, and send no emails.
- Such methods are flagged with the
@IsTestannotation in the method definition. - Unit test methods must be defined in test classes, that is, classes annotated with @IsTest.
- Such methods are flagged with the
- Unit tests must cover at least 75% of your Apex code, and all of those tests must complete successfully.
| Notes |
|---|
| When deploying Apex to a production organization, each unit test in your organization namespace is executed by default. |
| Calls to ```System.debug`` aren’t counted as part of Apex code coverage. |
| Test methods and test classes aren’t counted as part of Apex code coverage. |
| While at least 75% of your Apex code must be covered by tests, don’t focus on the percentage of code that is covered. Instead, make sure that every use case of your application is covered, including positive and negative cases, as well as bulk and single records. This approach ensures that 75% or more of your code is covered by unit tests. |
- Example
public static void updateOlderAccounts() {
// Get the 2 oldest accounts and change their description to 'Old Account'
Account[] oldAccounts = [SELECT Id, Description FROM Account ORDER BY CreatedDate ASC LIMIT 2];
// loop through them and update the Description field
for (Account acct : oldAccounts) {
acct.Description = 'Old Account';
}
// save the change you made
update oldAccounts;
}
// run it
updateOlderAccounts();
Demo
- Run the query to find the old accounts
cat oldAccounts.soql
SELECT Id, Description FROM Account ORDER BY CreatedDate ASC LIMIT 2
sfdx mohanc:data:query -u mohan.chinnappan.n.sel2@gmail.com -q oldAccounts.soql -f json
[
{
"attributes": {
"type": "Account",
"url": "/services/data/v57.0/sobjects/Account/0018W000024fLocQAE"
},
"Id": "0018W000024fLocQAE",
"Description": "Genomics company engaged in mapping and sequencing of the human genome and developing gene-based drugs"
},
{
"attributes": {
"type": "Account",
"url": "/services/data/v57.0/sobjects/Account/0018W000024fLoaQAE"
},
"Id": "0018W000024fLoaQAE",
"Description": "TODO"
}
]
cat UpdateOlderAccounts.cls
public static void updateOlderAccounts() {
// Get the 2 oldest accounts and change their description to 'Old Account'
Account[] oldAccounts = [SELECT Id, Description FROM Account ORDER BY CreatedDate ASC LIMIT 2];
// loop through them and update the Description field
for (Account acct : oldAccounts) {
acct.Description = 'Old Account';
}
// save the change you made
update oldAccounts;
}
// run it
updateOlderAccounts();
- Execute
sfdx mohanc:tooling:execute -u mohan.chinnappan.n.sel2@gmail.com -a UpdateOlderAccounts.cls
apexCode: public static void updateOlderAccounts() {
// Get the 2 oldest accounts and change their description to 'Old Account'
Account[] oldAccounts = [SELECT Id, Description FROM Account ORDER BY CreatedDate ASC LIMIT 2];
// loop through them and update the Description field
for (Account acct : oldAccounts) {
acct.Description = 'Old Account';
}
// save the change you made
update oldAccounts;
}
// run it
updateOlderAccounts();
compiled?: true
executed?: true
{
line: -1,
column: -1,
compiled: true,
success: true,
compileProblem: null,
exceptionStackTrace: null,
exceptionMessage: null
}
- Check the results after execution
sfdx mohanc:data:query -u mohan.chinnappan.n.sel2@gmail.com -q oldAccounts.soql -f json
[
{
"attributes": {
"type": "Account",
"url": "/services/data/v57.0/sobjects/Account/0018W000024fLocQAE"
},
"Id": "0018W000024fLocQAE",
"Description": "Old Account"
},
{
"attributes": {
"type": "Account",
"url": "/services/data/v57.0/sobjects/Account/0018W000024fLoaQAE"
},
"Id": "0018W000024fLoaQAE",
"Description": "Old Account"
}
]